The relationship between membrane and CO2
Sep 10, 2021In recent years, with the intensification of global warming, CO2, as the main greenhouse gas, has attracted widespread attention from all over the world. In order to alleviate the problem of global climate change brought about by CO2 emissions, "carbon peak" and "carbon neutrality" were formally proposed this year to achieve "carbon emission reduction". Human factors have led to a significant increase in the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. Among them, the CO2 emissions of coal-fired power plants account for about 1/3 of the world. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to remove a large amount of CO2 in the tail gas of coal-fired power plants.
At present, the industrial methods for removing CO2 from flue gas mainly include traditional techniques such as solvent absorption, membrane separation, pressure swing adsorption, and cryogenic distillation.
Fundamental
Membrane absorption method is a new type of separation process that combines membrane separation and ordinary absorption. Microporous membranes are mostly used. In this process, the gas-liquid two phases contact and mass transfer at the fixed gas-liquid interface, and flow on both sides respectively. The membrane itself has no selectivity to gas, and only serves to isolate the absorbent from the gas. CO2 diffuses through the membrane to the liquid side under the action of a concentration gradient. Theoretically, the membrane pores can allow gas molecules separated on one side of the membrane to penetrate to the other side of the membrane without high pressure, and the purpose of separating mixed gases is mainly achieved by the selective absorption of the absorbent.
The basic principle is shown in the figure below (take a hydrophobic porous membrane as an example). The driving force of this technology to achieve gas separation is the interphase concentration difference. The mass transfer process is based on Fick's law and can be divided into the following three steps: ① First, the solute is transferred from the mixed gas to the surface of the membrane pores; ② The solute is then transferred from the membrane pores Diffusion to the gas-liquid two-phase interface; ③The solute eventually reacts with the absorbent and is absorbed into the main body of the liquid phase.
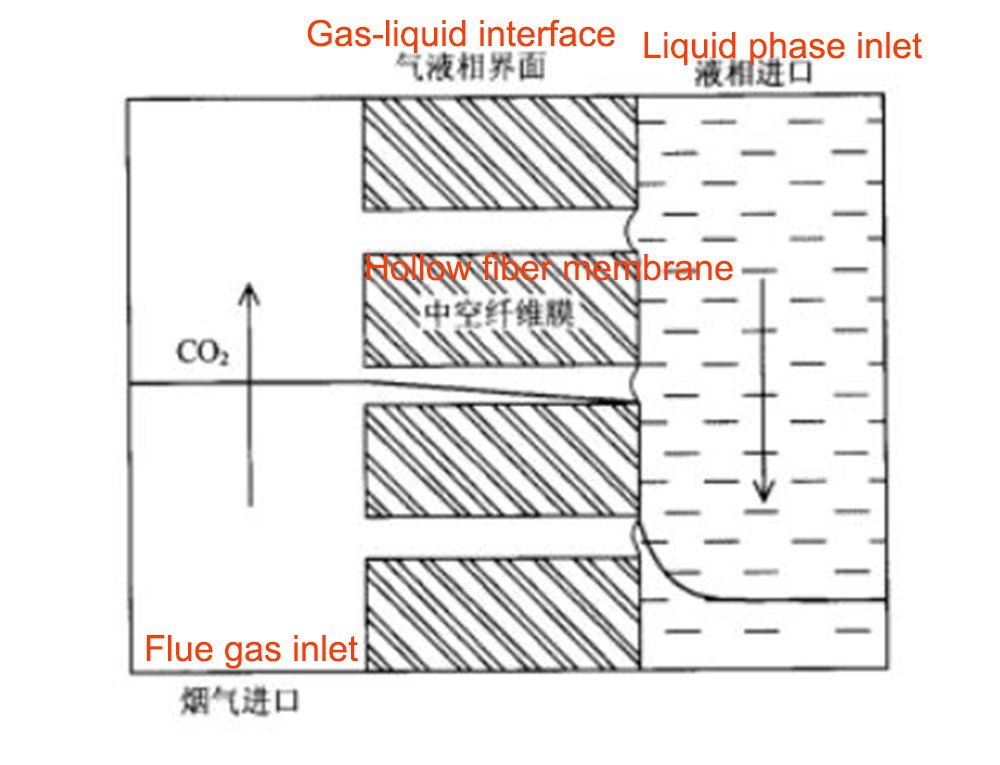
Different kinds of membranes for carbon dioxide absorption technology
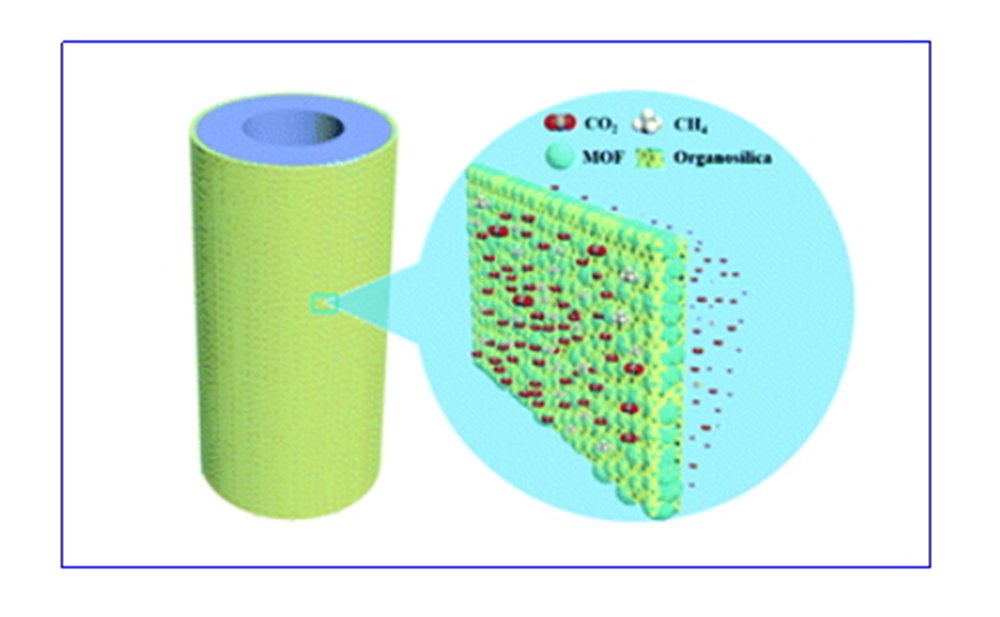
(1)The metal organic framework material (MOF) is compounded with organosilane, and a series of composite gas separation membranes with high flux and high selectivity have been successfully designed and prepared.
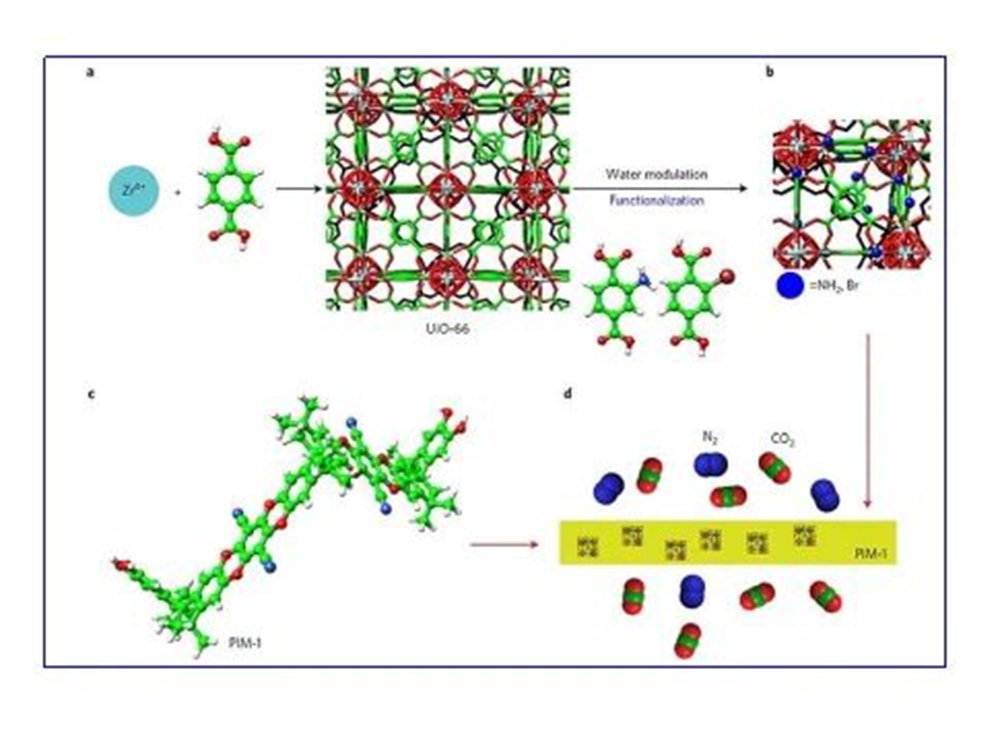
(2)Selecting microporous polymer (PIM-1) and metal organic framework material (MOF) nanoparticles to develop a new type of carbon dioxide separation membrane material in the form of mixed matrix membranes (MMMs), which has both high permeability and high Selective.
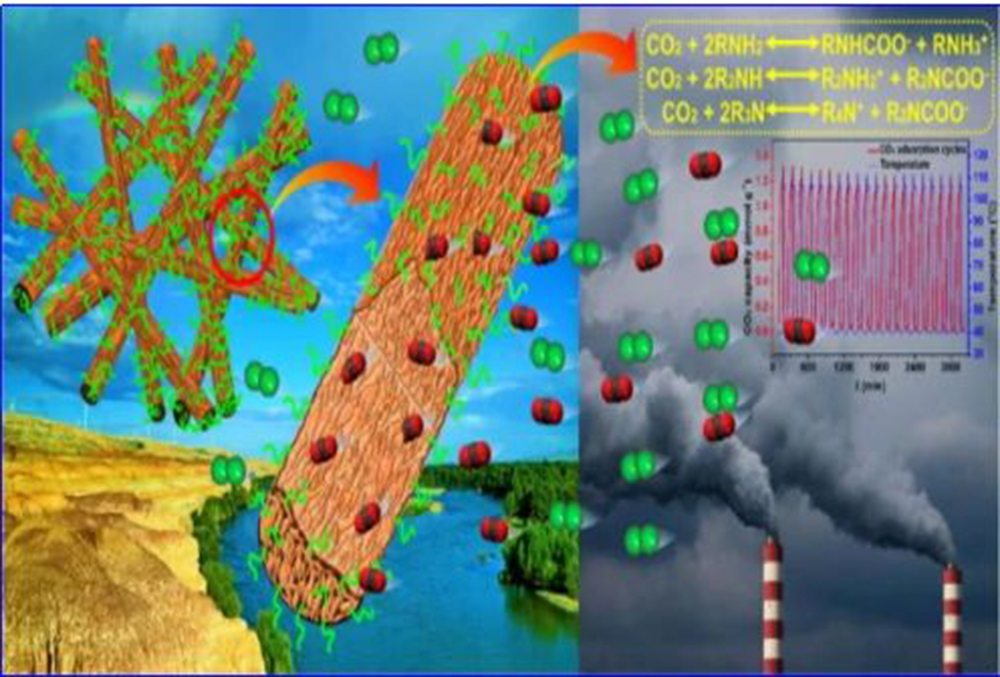
(3) The combination of electrospinning, pore formation, hydrolysis reaction and grafting technology successfully prepared a flexible and strong polyethyleneimine grafted polyacrylonitrile nanoporous fiber membrane (HPPAN-PEI).
Analysis of influencing factors
(1) Analysis of influence during mass transfer
A. CO2 ratio
According to the theory of double-membrane mass transfer, the higher the proportion of CO2, the thicker the gas-phase boundary layer, which hinders the diffusion of a large amount of CO2 in the membrane pores, thereby reducing the total mass transfer coefficient; and part of the CO2 leaves the membrane without completely reacting with the absorbent Contactor, the CO2 removal rate will also be reduced. However, as the volume fraction of CO2 increases, the concentration difference between phases of CO2 increases, thereby increasing the diffusion and mass transfer rate of CO2.
(2) Process factors
A. Membrane structure
Under the condition that the number and diameter of the hollow fiber membrane are fixed, the increase of the length of the fiber membrane increases the surface area of the membrane, which in turn increases the residence time of CO2 in the liquid phase, which is conducive to the full absorption reaction. However, if the membrane column is too long, the absorption liquid will become saturated, which will reduce the driving force of gas-liquid mass transfer and decrease the mass transfer efficiency.
B. Membrane material
The membrane materials are mainly organic polymer membranes, inorganic membranes, and organic-inorganic composite membranes. Among them, the widely used membrane materials are polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polysulfone (PS), polyethersulfone (PES), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), etc. . Various membrane materials currently used are all hydrophobic membrane materials, so that the gas phase fills the hollow fiber membrane pores during the absorption process and has a larger contact area than hydrophilic membrane materials. The hollow fiber membrane modules use different membrane materials. Among them, polypropylene membranes are widely used in industry due to their cheap material prices. The PTFE membrane exhibits good mechanical properties and self-lubricating properties, high and low temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, and is superior to other membrane materials.
C. Absorbent
The absorbent used in membrane absorption has evolved from water, strong alkali solutions, and inorganic salt solutions to traditional alcohol amine solutions, and then to mixed absorbents containing additives or several solutions. The following figure shows the advantages and disadvantages of each absorbent.