Demystifying the tensile properties of PPS filter media
Mar 01, 2022Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) fiber filter material is widely used in industrial furnace kiln flue gas bag filter. It needs to bear various loads during service in complex working conditions, and tensile load is the most common. The PPS fiber is combed by the carding machine, and the axial direction of the single fiber is consistent with the axial direction of the fiber web, and the fibers are connected end to end to form a single-layer fiber web.
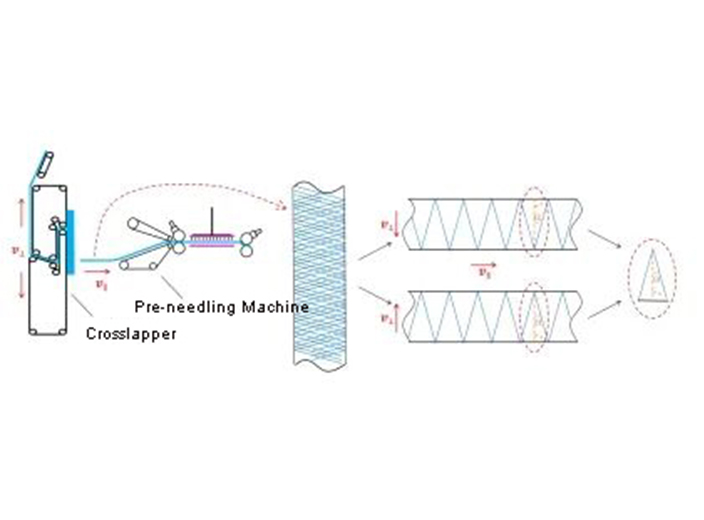
The fiber web is reciprocally laid with the laying trolley (the speed of the laying trolley is ), and it moves forward with the conveying curtain (the speed is ), so that the fiber axis (web axis) and the filter material axis (fiber axis) are cross-laid. direction of web movement) at an angle (fiber orientation angle).
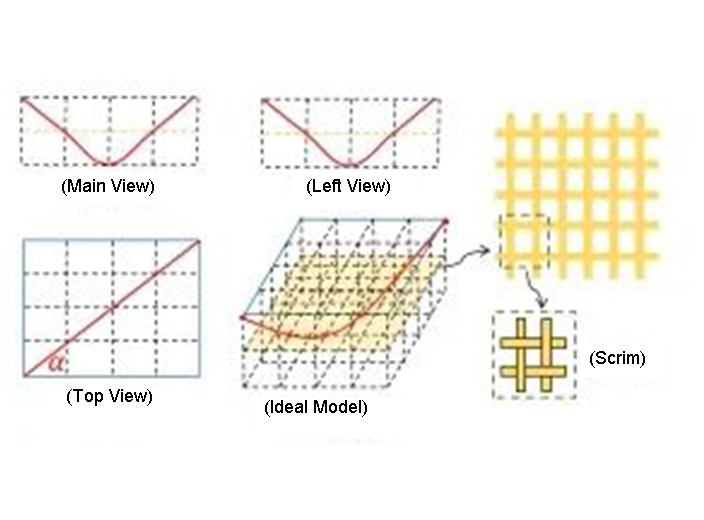
After calculation, the orientation angle of the PPS fiber produced by Yuanchen Technology is 5°. It can be seen that the fiber orientation in the filter material is almost the same as that of the filter material in the transverse direction. After acupuncture, the transverse strength must be much greater than the longitudinal direction. Therefore, a plain woven fabric needs to be added between the two layers of fiber webs to provide warp strength. In fact, the PPS fibers are not completely straight and parallel to each other after being combed by the carding machine. After the two layers of fiber webs and the base fabric are entangled by needle punching, with the drafting of the filter material, the single fibers are in the filter material structure. The mid-space state is more complex and difficult to model structurally.
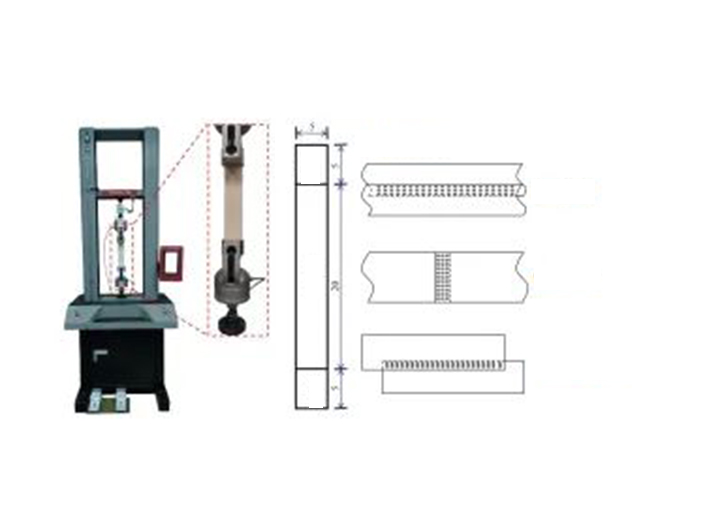
According to GB/T 6719 (Technical requirements for bag filter) and GB/T 3923.1 (Determination of tensile strength and elongation at break of textile fabrics Part 1 (strip method)), PPS filter is used for bag filter. material samples for testing.
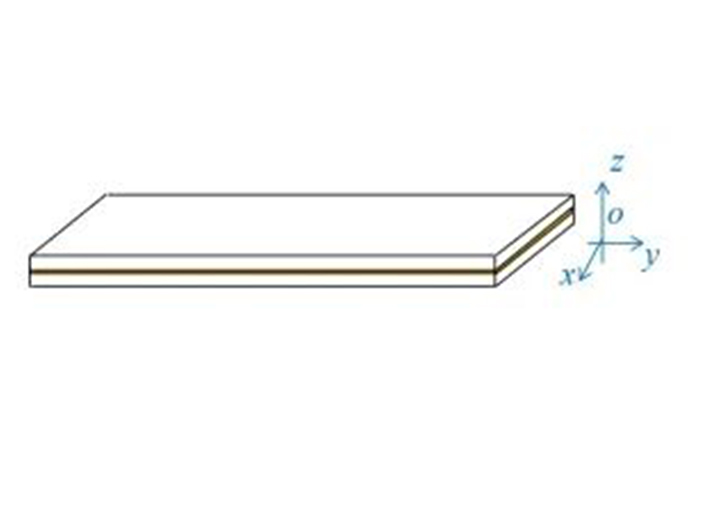
From a macroscopic point of view, the spatial path and entanglement of fibers are ignored, and the filter material is regarded as a whole. Different from ordinary two-dimensional fabrics, the filter material has a tertiary structure of "fiber layer-base fabric layer-fiber layer" in the thickness direction, and the thickness cannot be ignored, so it can be considered as a three-dimensional fabric. Since the structure of the filter material in the x, y, and z directions is different, the filter material is an orthotropic material.
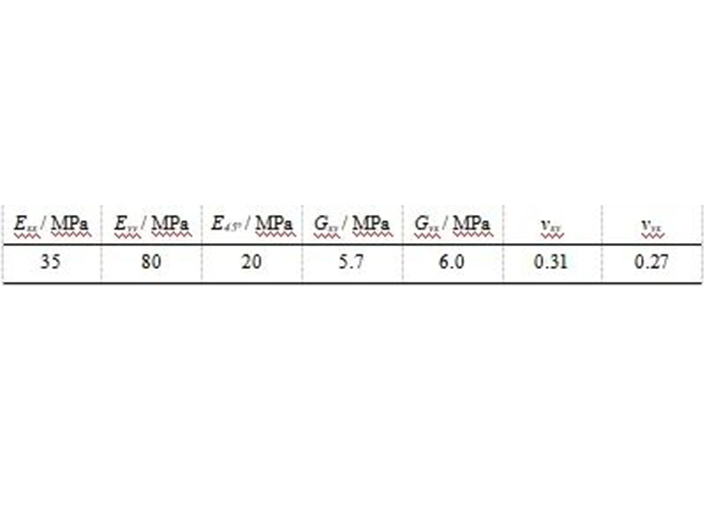
The basic elastic parameters of the filter material are shown in the table.
1. Seamless line pattern
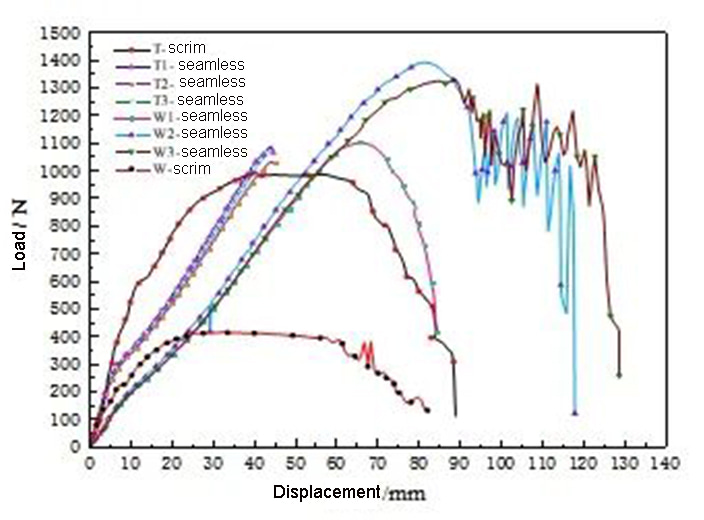
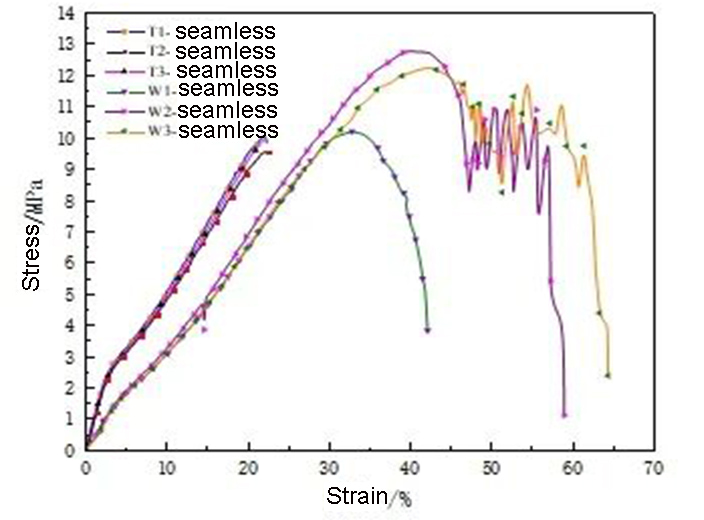
The peak load of the PPS filter material in the warp direction is about 1100N, and the peak stress is about 10MPa; the peak load of the filter material in the weft direction is about 1300N, and the peak stress is about 13MPa. For warp stretching, the stretching behavior of the filter material is divided into three stages. In the first stage, the base cloth mainly bears the load, and the fibers hardly work; in the second stage, the composite structure composed of the fiber aggregate and the base cloth bears the load together; bear the load. For weft stretching, the stretching curve of the filter material is also divided into three stages. In the first stage, the fiber and the base fabric share the load; in the second stage, the tightly cohesive needle-punched oriented fibers mainly bear the load; in the third stage, the base fabric is not enough to bear the load and begins to break, and the curve shows a jagged "jitter" , until the filter material fails as a whole.
2, with seam pattern
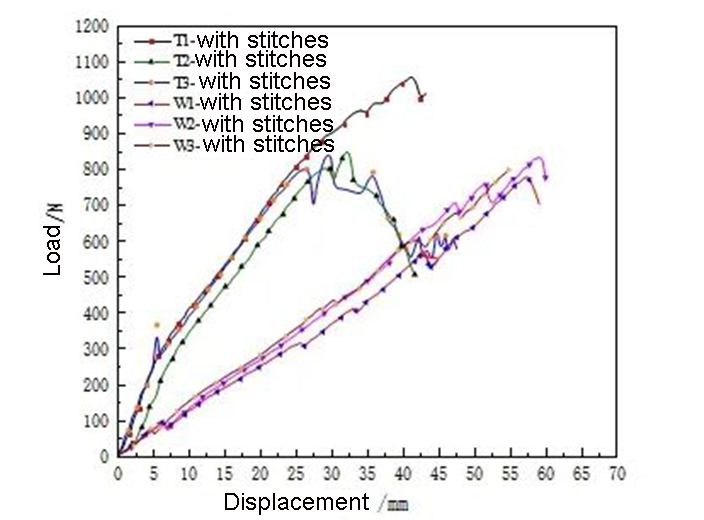
Stitch-like stretching essentially relies on the strength of the stitches or the shearing action between the stitches and the filter material. The meridional stretching is divided into three stages. First, the elastic stage has a large modulus. After reaching the yield point, it enters the plastic deformation stage. The modulus decreases and the load increases further until the sutures are broken one by one. During weft stretching, the number of stitches is small, and the stretching process can be divided into two stages. In the elastic stage, the modulus remains unchanged, and the load increases all the time. After reaching a certain level, the stitches are gradually embedded in the filter material. Break one by one until the filter material fails.
3. Shearing conditions
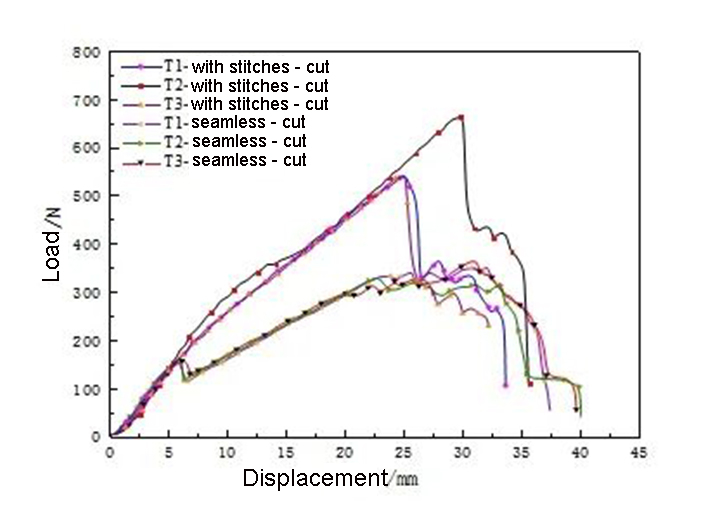
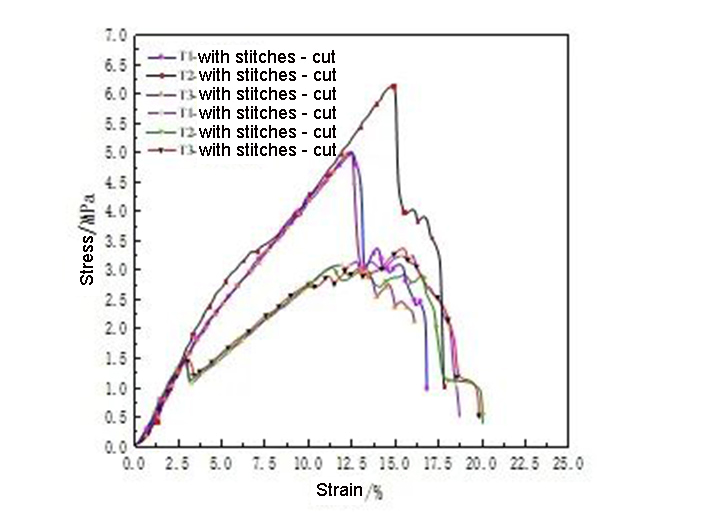
The essence of shear strip stretching is shear stretching, not axial stretching. The initial shear tensile modulus of the seamless and sutured filter media is the same; after the strain reaches about 2.6%, the sutured thread relies on the interlocking effect of the sutures, the modulus is large, the bearing capacity is strong, and the peak value The load is about 680N; the seamless pattern has no limit, the filter material is torn until shearing, the modulus is low, and the peak load is about 350N, and then the base fabric is broken one by one. Therefore, during the service process of the filter material, it should be ensured that the force of the filter material is uniform, so as to avoid the shear effect and the failure of the filter material.