Common fiber raw materials
Feb 22, 2022Fiber is the most basic raw material for non-woven materials. Since non-woven materials are different from traditional textiles, which are formed by the arrangement and combination of yarns, they are fiber aggregates directly composed of fiber raw materials. have a more direct impact.
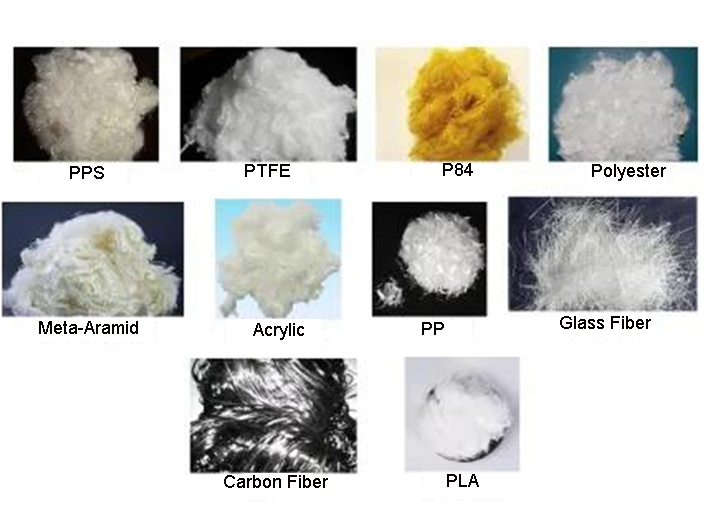
The fiber raw materials used by non-woven technology are very wide. To produce non-woven products with reasonable performance and price ratio, it is necessary to first understand the role of fibers in non-woven materials, master the basic properties of fibers, and determine the basic properties of fibers according to non-woven processing technology and post-processing technology. and equipment to properly select fiber raw materials. Common fiber raw materials are shown in the figure below.

The properties of nonwovens are related to many factors, the most important of which are the properties of the fibers. The influence of fibers on the properties of non-woven materials is mainly reflected in two aspects, on the one hand, the material properties directly expressed by fibers through different non-woven structures; on the other hand, the processing adaptability of fibers in non-woven processing. Also affects the final properties of the nonwoven.
1. The effect of fiber appearance on the properties of nonwovens
The apparent properties of fibers mainly include length, linear density, crimp, cross-sectional shape and surface friction properties, etc. Their effects on the properties of non-woven materials are discussed as follows:
1. Fiber length and length distribution
Long fiber length is beneficial to improve the strength of non-woven materials, which is mainly due to the increase of cohesion between fibers, the increase of entanglement points, the enhancement of entanglement effect, and the improvement of the utilization degree of fiber strength. In the production of bonding method, the fiber length is long, which is also manifested as increased bond points, enhanced adhesion, and increased strength of nonwovens.
2. Fiber linear density
The fiber linear density is small, the obtained non-woven material has high bulk density, high strength and soft hand feeling. Under the condition of the same areal density of non-woven materials, the smaller the fiber linear density, the more fibers, and the contact point and contact area between fibers increase, which increases the bonding area between fibers or increases the bonding area between fibers. Slip resistance, thereby increasing the strength of the nonwoven. However, too fine fibers will cause difficulties in opening, carding and web formation. The fiber linear density generally used in non-woven materials is 1.2~33dtex. Generally, crude fibers are mostly used in carpets and pads, and the main consideration is to improve the elasticity of non-woven materials. For some filter materials, fiber blending or gradient distribution with various linear density specifications from fine to coarse is required to improve filtration performance.
3. Fiber curl
Fiber crimp has a certain influence on the uniformity of the fiber web, and on the strength, elasticity and feel of the non-woven material. When the fibers are more crimped, the cohesion force between the fibers is large, and it is not easy to break the web when the web is formed, the uniformity is good, and the conveying or folding processing is also smoother. During the bonding process, due to the high degree of fiber curl, the fibers between the bonding points can maintain a certain elastic elongation, so that the product feels soft and elastic. In non-woven materials such as needle punching reinforcement and stitchbonding, the higher the fiber crimp, the greater the cohesion force, which increases the sliding resistance between fibers and improves the strength and elasticity of the product.
Among natural fibers, cotton fibers have natural crimps, and there are many mature and normal crimps; wool fibers also have periodic natural crimps. Chemical fibers can be crimped by extrusion with a crimping machine during the manufacturing process. Generally, the number of crimps per centimeter is 4 to 6.
4. Fiber cross-sectional shape
The cross-sectional shape of the fiber has a certain influence on the stiffness, elasticity, adhesion and gloss of the nonwoven material. Natural fibers have their own naturally formed cross-sectional shapes. For example, cotton fibers are round with a waist and have a central cavity; silk is an irregular triangle; shape, hollow shape, etc. Different cross-sectional shapes directly affect product performance. For example, fibers with triangular cross-sections have higher stiffness than fibers with circular cross-sections, while fibers with elliptical cross-sections have lower stiffness than circular cross-section fibers. The hollow fiber has excellent rigidity, good fluffiness and warmth retention. When processing chemically bonded non-woven materials, the shape of the fiber cross-section is closely related to the contact area of the adhesive. For example, the surface area of the star-shaped cross-section fiber is about 50% larger than that of the circular cross-section fiber of the same linear density. The larger the area, the greater the adhesion. The low bending stiffness of the flat-section fibers increases the hydroentanglement effect and improves the mechanical properties. A certain optical effect can be obtained by the reflection of light on the surface of the fiber with special-shaped section. For example, the triangular section (similar to silk section) is like countless triangular prisms in the product. The various colors they separate can produce a soft luster.

5. Friction factor of fiber surface
The friction factor of the fiber surface not only affects the performance of the product, but also affects the processing technology. For mechanically reinforced non-woven materials such as needle punching and stitching, the friction coefficient of the fiber surface is large, and the fiber slip resistance is also large, which is conducive to improving the strength of the product. However, if the friction factor is too large, it will increase the acupuncture resistance, make puncture difficult, and cause failures such as needle breakage. In addition, synthetic fibers have a large friction factor, which is easy to cause static electricity generation and accumulation, which affects the normal progress of carding and web formation. Therefore, synthetic fibers are usually surface-treated with an antistatic agent or a balance of temperature and humidity in advance.
2. Influence of physical and mechanical properties and chemical properties of fibers on the properties of non-woven materials
The physical and mechanical properties and chemical properties of fibers mainly include breaking strength and elongation, initial transverse weight, elastic recovery, resistance to easy winding and abrasion, moisture absorption, thermal properties, chemical resistance and aging resistance. These properties directly affect the performance of nonwovens, and the following highlights several properties that affect the suitability of fibers for processing.
1. Mechanical properties of fibers
During nonwoven processing, fibers are stretched, bent, compressed, rubbed and twisted to produce different deformations. During the use of non-woven materials, the main external force is tension, and the bending properties of fibers are also related to their tensile properties. Therefore, tensile properties are the most important mechanical properties of fibers, also known as mechanical properties.
2. Fiber hygroscopicity
Fiber hygroscopicity refers to the fiber's ability to absorb moisture in the vapor phase or aqueous solution in the air, and the ability to absorb moisture is different. Most synthetic fibers have poor hygroscopic ability and belong to hydrophobic fibers. Fiber hygroscopicity has a significant impact on the processing technology of non-woven materials. In chemical bonding method and spunlace non-woven processing technology, the hygroscopicity of fiber is particularly important. Generally speaking, the fiber web composed of fibers with good hygroscopicity is conducive to the uniform dispersion of the adhesive in the fiber web, and the bonding effect is good. Fibers with good hygroscopicity are easily entangled during the hydroentanglement process, which can improve the mechanical properties of the final nonwoven material. In dry-laid and needle-punched reinforcement, the fiber moisture absorption is too low, the fiber is easy to break and easy to generate static electricity, the moisture absorption is too high, and the fiber is easy to wind up machinery.
3. Thermal properties of fibers
Different temperature environments are encountered during the processing and use of non-woven materials, and the temperature range is wide. During the chemical bonding process, the thermal effect of the fiber web through the drying and baking process will change the flexibility, aggregated structure and macroscopic shape of the fiber polymer to varying degrees, thereby affecting the nonwoven processing and product performance. Therefore, for the thermal bonding process, the melting point, glass transition temperature, softening point, decomposition point, heat shrinkage, and heat resistance of the fiber must be considered. The long-term use temperature and instantaneous use temperature of commonly used fibers are shown in the figure below.
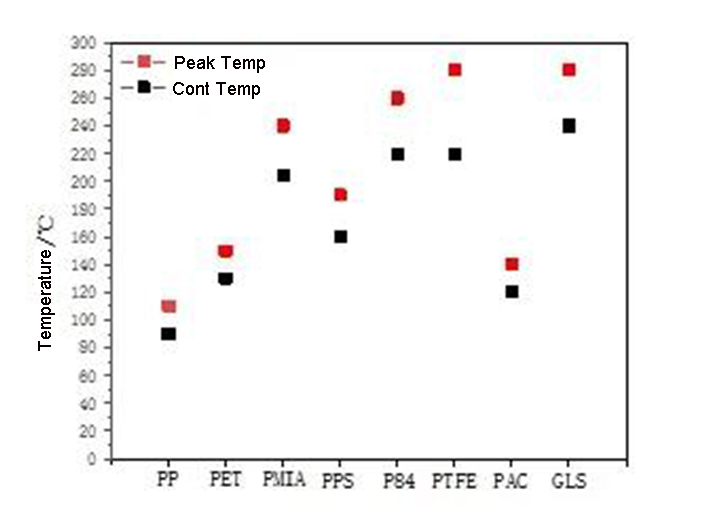
Understanding the influence factors of fiber raw materials on non-woven materials can better select suitable fibers, suitable processes and suitable post-treatment methods according to the working conditions, so as to prepare high-efficiency dust removal filter bags with excellent performance. Anhui Yuanchen Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. has been committed to the development of high-efficiency dust filter bags for many years, and can design and produce suitable dust filter bags according to working conditions.